用Visual C#实现局域网点对点通讯
点对点即Peer-To-Peer,通常简写为P2P。所谓网络中的点对点,其实可以看成是一种对等的网络模型。P2P其实是实现网络上不同计算机之间,不经过中继设备直接交换数据或服务的一种技术。P2P由于允许网络中任一台计算机可以直接连接到网络中其他计算机,并与之进行数据交换,这样既消除了中间环节,也使得网络上的沟通变得更容易、更直接。
P2P作为一种网络的模型,它有别于传统的客户/服务器模型。客户/服务器模型一般都有预定义的客户机和服务器。而在P2P模型转并没有明确的客户端和服务器,但其实在P2P模型中,每一台计算机既可以看成是服务器,也可以看成是客户机。在网络中,传统上的客户机/服务器通讯模型中,发送服务请求或者发送数据的计算机,一般称为客户机;而接收、处理服务或接收数据的计算机称为服务器。而在P2P网络模型中,计算机不仅接收数据,还有发送数据,不仅提出服务请求,还有接收对方的服务请求。
在下面介绍的用Visual C#实现的局域网点对点通讯程序,就有如下特点,在网络利用此通讯程序进行通讯的任一计算机,在通讯之前,都需要侦听端口号,接受其他机器的连接申请,并在连接建立后,就可以接收对方发送来的数据;同时也可以向其他机器提出连接申请,并在对方计算机允许建立连接请求后,发送数据到对方。可见在网络中利用此软件进行P2P网络通讯的任一计算机既是客户机,同样也是服务器。
一.程序的设计、调试、运行的软件环境
(1).微软公司视窗2000服务器版
(2).Visual Studio .Net正式版,.Net FrameWork SDK版本号3705
二.关键步骤及其解决方法: 关键步骤就是实现信息在网络中的发送和接收。数据接收使用的是Socket,数据发送使用的是NetworkStream
1.利用Socket来接收信息
为了更清楚的说明问题,程序在处理数据发送和接收时采用了不通的端口号,发送数据程序在缺省状态设定的端口号为"8889"。下面代码是侦听端口号"8889",接受网络中对此端口号的连接请求,并在建立连接后,通过Socket接收远程计算机发送来的数据:
try
{
TcpListener tlListen1 = new TcpListener(8889);
//侦听端口号
tlListen1.Start();
Socket skSocket = tlListen1.AcceptSocket();
//接受远程计算机的连接请求,并获得用以接收数据的Socket实例
EndPoint tempRemoteEP = skSocket.RemoteEndPoint;
//获得远程计算机对应的网络远程终结点
while (true)
{
Byte[] byStream = new Byte[80];
//定义从远程计算机接收到数据存放的数据缓冲区
int i = skSocket.ReceiveFrom(byStream, ref tempRemoteEP);
//接收数据,并存放到定义的缓冲区中
string sMessage = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(byStream);
//以指定的编码,从缓冲区中解析出内容
MessageBox.Show(sMessage);
//显示传送来的数据
}
}
catch (System.Security.SecurityException)
{
MessageBox.Show("防火墙安全错误!", "错误",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
}
2.利用NetworkStream来传送信息
在使用StreamWriter处理NetworkStream传送数据时,数据传送的编码类型是"UTF8",下列代码是对IP地址为"10.138.198.213"的计算机的"8888"端口号提出连接申请,并在连接申请建立后,以UTF8编码发送字符串"您好,见到您很高兴"到对方,由于下列代码中的注释比较详细,这里就不具体介绍了,下列代码也是使用NetworkStream传送数据的典型代码:
try
{
TcpClient tcpc = new TcpClient("10.138.198.213", 8888);
//对IP地址为"10.138.198.213"的计算机的8888端口提出连接申请
NetworkStream tcpStream = tcpc.GetStream();
//如果连接申请建立,则获得用以传送数据的数据流
}
catch (Exception)
{
MessageBox.Show("目标计算机拒绝连接请求!");
break;
}
try
{
string sMsg = "您好,见到您很高兴";
StreamWriter reqStreamW = new StreamWriter(tcpStream);
//以特定的编码往向数据流中写入数据 ,默认为UTF8编码
reqStreamW.Write(sMsg);
//将字符串写入数据流中
reqStreamW.Flush();
//清理当前编写器的所有缓冲区,并使所有缓冲数据写入基础流
}
catch (Exception)
{
MessageBox.Show("无法发送信息到目标计算机!");
}
当然在具体用Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯程序时,还必须掌握很多其他方面的知识,如资源的回收。在用Visual C#编写网络应用程序的时候,很多朋友遇到这样的情况。当程序退出后,通过Windows的"资源管理器"看到的是进程数目并没有减少。这是因为程序中使用的线程可能并没有有效退出。虽然Thread类中提供了"Abort"方法用以中止进程,但并不能够保证成功退出。因为进程中使用的某些资源并没有回收。在某些情况下垃圾回收器也不能保证完全的回收资源,还是需要我们自己手动回收资源的。在本文介绍的程序中也涉及到资源手动回收的问题。实现方法可参阅下面具体实现步骤中的第十二步。
三.具体步骤
在了解、掌握了上面的关键问题及其解决方法后,再实现用Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯程序相对就容易许多,下面是具体的实现步骤:
启动Visual Studio .Net,并新建一个Visual C#项目,名称为【Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯程序】。
在Visual Studio .Net集成开发环境中的【解决方案资源管理器】窗口中,双击Form1.cs文件,进入Form1.cs文件的编辑界面。
在Form1.cs文件的开头,用下列导入命名空间代码替代系统缺省的导入命名空间代码。
using System; using System.Drawing; using System.Collections; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Data; using System.Net.Sockets; using System.Net; using System.IO; using System.Text; using System.Threading;再把Visual Studio.Net的当前窗口切换到【Form1.cs(设计)】窗口,并从【工具箱】中的【Windows窗体组件】选项卡中往窗体中拖入下列组件:
四个Button组件;二个ListBox组件;四个TextBox组件;一个StatusBar组件;五个Label组件。并在四个Button组件拖入窗体后,分别在窗体设计界面中双击它们,则系统会在Form1.cs文件中分别产生这四个组件的Click事件对应的处理代码。
在【解决方案资源管理器】窗口中,双击Form1.cs文件,进入Form1.cs文件的编辑界面。以下面代码替代系统产生的InitializeComponent过程。下面代码是对上面添加的组件进行初始化:
private void InitializeComponent() { this.listBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.ListBox(); this.textBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.label3 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.label2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.textBox3 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.textBox2 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.label1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.label4 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.label5 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.button2 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.button3 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.button4 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button(); this.textBox4 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.statusBar1 = new System.Windows.Forms.StatusBar(); this.statusBarPanel1 = new System.Windows.Forms.StatusBarPanel(); this.statusBarPanel2 = new System.Windows.Forms.StatusBarPanel(); this.label6 = new System.Windows.Forms.Label(); this.listBox2 = new System.Windows.Forms.ListBox(); ((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize) (this.statusBarPanel1)).BeginInit(); ((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize) (this.statusBarPanel2)).BeginInit(); this.SuspendLayout(); this.listBox1.ItemHeight = 12; this.listBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(122, 110); this.listBox1.Name = "listBox1"; this.listBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(212, 88); this.listBox1.TabIndex = 4; this.textBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(122, 18); this.textBox1.Name = "textBox1"; this.textBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(210, 21); this.textBox1.TabIndex = 1; this.textBox1.Text = ""; this.label3.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(220, 52); this.label3.Name = "label3"; this.label3.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(66, 23); this.label3.TabIndex = 7; this.label3.Text = "本地端口:"; this.label2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(38, 54); this.label2.Name = "label2"; this.label2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 23); this.label2.TabIndex = 20; this.label2.Text = "远程端口号:"; this.textBox3.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(294, 50); this.textBox3.Name = "textBox3"; this.textBox3.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(38, 21); this.textBox3.TabIndex = 3; this.textBox3.Text = "8889"; this.button1.FlatStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle.Flat; this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(348, 16); this.button1.Name = "button1"; this.button1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(92, 40); this.button1.TabIndex = 6; this.button1.Text = "连接远程机"; this.button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button1_Click); this.textBox2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(122, 50); this.textBox2.Name = "textBox2"; this.textBox2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(38, 21); this.textBox2.TabIndex = 2; this.textBox2.Text = "8888"; this.label1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(38, 22); this.label1.Name = "label1"; this.label1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 23); this.label1.TabIndex = 16; this.label1.Text = "远程IP地址:"; this.label4.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, 84); this.label4.Name = "label4"; this.label4.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(66, 23); this.label4.TabIndex = 23; this.label4.Text = "发送信息:"; this.label5.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(36, 112); this.label5.Name = "label5"; this.label5.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 23); this.label5.TabIndex = 24; this.label5.Text = "发送的信息:"; this.button2.Enabled = false; this.button2.FlatStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle.Flat; this.button2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(352, 192); this.button2.Name = "button2"; this.button2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(92, 40); this.button2.TabIndex = 7; this.button2.Text = "断开连接"; this.button2.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button2_Click); this.button3.FlatStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle.Flat; this.button3.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(348, 74); this.button3.Name = "button3"; this.button3.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(92, 40); this.button3.TabIndex = 8; this.button3.Text = "侦听端口"; this.button3.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button3_Click); this.button4.Enabled = false; this.button4.FlatStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FlatStyle.Flat; this.button4.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(350, 132); this.button4.Name = "button4"; this.button4.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(92, 40); this.button4.TabIndex = 9; this.button4.Text = "发送信息"; this.button4.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.button4_Click); this.textBox4.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(122, 82); this.textBox4.Name = "textBox4"; this.textBox4.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(212, 21); this.textBox4.TabIndex = 25; this.textBox4.Text = ""; this.statusBar1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(0, 301); this.statusBar1.Name = "statusBar1"; this.statusBar1.Panels.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.StatusBarPanel[] { this.statusBarPanel1 ,this.statusBarPanel2}); this.statusBar1.ShowPanels = true; this.statusBar1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(456, 22); this.statusBar1.TabIndex = 26; this.statusBarPanel1.Width = 200; this.statusBarPanel2.Width = 230; this.label6.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(48, 210); this.label6.Name = "label6"; this.label6.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(66, 23); this.label6.TabIndex = 28; this.label6.Text = "接收信息:"; this.listBox2.ItemHeight = 12; this.listBox2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(122, 206); this.listBox2.Name = "listBox2"; this.listBox2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(214, 88); this.listBox2.TabIndex = 27; this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(6, 14); this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(456, 323); this.Controls.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.Control[] { this.label6 , this.listBox2 , this.statusBar1 , this.textBox4 , this.button4 , this.button3 , this.button2 , this.label5 , this.label4 , this.label2 , this.textBox3 , this.button1 , this.textBox2 , this.label1 , this.label3 , this.textBox1 , this.listBox1}); this.FormBorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle. FixedSingle; this.MaximizeBox = false; this.Name = "Form1"; this.Text = "Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯程序"; this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Form1_Load); ((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize) (this.statusBarPanel1)).EndInit(); ((System.ComponentModel.ISupportInitialize) (this.statusBarPanel2)).EndInit(); this.ResumeLayout(false); }至此,【Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯程序】项目的界面设计和功能实现的前期工作就完成了,设计界面如图1所示:
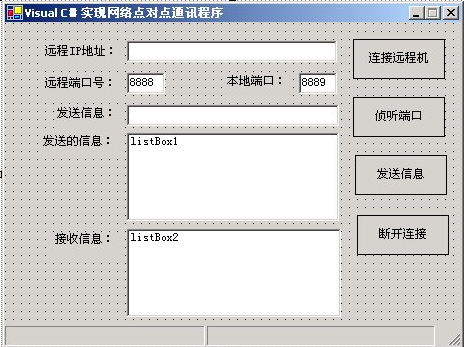
图1 项目的设计界面在【解决方案资源管理器】窗口中,双击Form1.cs文件,进入Form1.cs文件的编辑界面。并在定义Form类成员代码区中,加入下列代码,下列代码的作用是定义程序中使用的全局变量。
private Thread th; //创建线程,用以侦听端口号,接收信息 private TcpListener tlListen1; //用以侦听端口号 private bool listenerRun = true; //设定标示位,判断侦听状态 private NetworkStream tcpStream; //创建传送/接收的基本数据流实例 private StreamWriter reqStreamW; //用以实现向远程主机传送信息 private TcpClient tcpc; //用以创建对远程主机的连接 private Socket skSocket; //用以接收远程主机传送来的数据用下列代码替换Form1.cs中的button1组件的"Click"事件对应的代码,下列代码的作用是向远程计算机提出连接申请,如果连接建立,则获得传送数据的数据源:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { try { tcpc = new TcpClient(textBox1.Text, Int32.Parse(textBox3.Text)); //向远程计算机提出连接申请 tcpStream = tcpc.GetStream(); //如果连接申请建立,则获得用以传送数据的数据流 statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "成功连接远程计算机!"; button2.Enabled = true; button1.Enabled = false; button4.Enabled = true; } catch (Exception) { statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "目标计算机拒绝连接请求!"; } }在Form1.cs中的Main函数之后,添加下列代码,下面代码是定义一个名称为"Listen"的过程:
private void Listen() { try { tlListen1 = new TcpListener(Int32.Parse(textBox2.Text)); tlListen1.Start(); //侦听指定端口号 statusBar1.Panels[1].Text = "正在监听..."; //接受远程计算机的连接请求,并获得用以接收数据的Socket实例 skSocket = tlListen1.AcceptSocket(); //获得远程计算机对应的网络远程终结点 EndPoint tempRemoteEP = skSocket.RemoteEndPoint; IPEndPoint tempRemoteIP = (IPEndPoint)tempRemoteEP; IPHostEntry host = Dns.GetHostByAddress (tempRemoteIP.Address); string HostName = host.HostName; //根据获得的远程计算机对应的网络远程终结点获得远程计算机的名称 statusBar1.Panels[1].Text = "'" + HostName + "' " + "远程计算机正确连接!"; //循环侦听 while (listenerRun) { Byte[] stream = new Byte[80]; //定义从远程计算机接收到数据存放的数据缓冲区 string time = DateTime.Now.ToString(); //获得当前的时间 int i = skSocket.ReceiveFrom(stream, ref tempRemoteEP); //接收数据,并存放到定义的缓冲区中 string sMessage = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8. GetString(stream); //以指定的编码,从缓冲区中解析出内容 listBox2.Items.Add(time + "" + HostName + ":"); listBox2.Items.Add(sMessage); //显示接收到的数据 } } catch (System.Security.SecurityException) { MessageBox.Show("防火墙安全错误!", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation); } }用下列代码替换Form1.cs中的button2组件的Click事件对应的处理代码,下列代码的作用是断开当前的连接:
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { listenerRun = false; tcpc.Close(); statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "断开连接!"; button1.Enabled = true; button2.Enabled = false; button4.Enabled = false; }用下列代码替换Form1.cs中的button3组件的Click事件对应的处理代码,下列代码的作用是以上面定义的Listen过程来初始化线程实例,并启动线程,达到侦听端口的目的:
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Listen)); //以Listen过程来初始化线程实例 th.Start(); //启动此线程 }用下列代码替换Form1.cs中的button4组件的Click事件对应的处理代码,下列代码的作用是向远程计算机的指定端口号发送信息。
private void button4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { try { string sMsg = textBox4.Text; string MyName = Dns.GetHostName(); //以特定的编码往向数据流中写入数据, //默认为UTF8Encoding 的实例 reqStreamW = new StreamWriter(tcpStream); //将字符串写入数据流中 reqStreamW.Write(sMsg); //清理当前编写器的所有缓冲区,并使所有缓冲数据写入基础流 reqStreamW.Flush(); string time = DateTime.Now.ToString(); //显示传送的数据和时间 listBox1.Items.Add(time + " " + MyName + ":"); listBox1.Items.Add(sMsg); textBox4.Clear(); } //异常处理 catch (Exception) { statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "无法发送信息到目标计算机!"; } }用下列代码替换Form1.cs中的"Dispose"过程对应的处理代码,下列代码的作用是在程序退出后,清除没有回收的资源:
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) { try { listenerRun = false; th.Abort(); th = null; tlListen1.Stop(); skSocket.Close(); tcpc.Close(); } catch { } if (disposing) { if (components != null) { components.Dispose(); } } base.Dispose(disposing); }运行程序,实现网络点对点通讯:
单击快捷键F5编译成功后,把此程序分发到网络中的二台计算机中。在正确输入侦听端口号、远程计算机IP地址、远程端口号输入正确后,单击【侦听端口】和【连接远程机】按钮建立聊天的连接。就通过【发送信息】按钮进行聊天了。图2是通讯时运行界面。
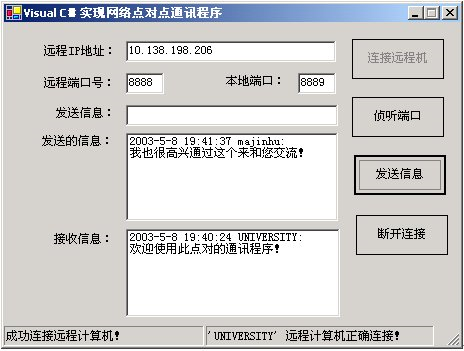
图2 运行界面
五.总结
网络点对点通讯程序并不像客户端/服务器端模型程序那样,分成客户端程序和服务器端程序。它是集客户端程序和服务器端程序与一身,所以在具体的程序设计中就相对麻烦一点。上面介绍的在用Visual C#实现网络点对点通讯的示例虽然结构并不复杂,但涉及的知识面却比较广泛。如示例中涉及到许多很多网络功能的实现,如:侦听端口号、建立连接、发送数据和接收数据等,还涉及到线程的处理、资源的回收等。了解、掌握这些问题的处理方法对编写更复杂的网络应用程序是十分必要的。
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
private Thread th; //创建线程,用以侦听端口号,接收信息
private TcpListener tlListen1; //用以侦听端口号
private bool listenerRun = true; //设定标示位,判断侦听状态
private NetworkStream tcpStream; //创建传送/接收的基本数据流实例
private StreamWriter reqStreamW; //用以实现向远程主机传送信息
private TcpClient tcpc; //用以创建对远程主机的连接
private Socket skSocket;//用以接收远程主机传送来的数据
// 清理所有正在使用的资源
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
try
{
listenerRun = false;
th.Abort();
th = null;
tlListen1.Stop();
skSocket.Close();
tcpc.Close();
}
catch { }
}
//连接远程机
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
tcpc = new TcpClient(textBox1.Text, int.Parse(textBox2.Text)); //向远程计算机提出连接申请
tcpStream = tcpc.GetStream(); //如果连接申请建立,则获得用以传送数据的数据流
statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "成功连接远程计算机!";
button2.Enabled = true;
button1.Enabled = false;
button4.Enabled = true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "目标计算机拒绝连接请求!";
}
}
//侦听方法
private void Listen()
{
try
{
tlListen1 = new TcpListener(int.Parse(textBox3.Text));
tlListen1.Start(); //侦听指定端口号
statusBar1.Panels[1].Text = "正在监听...";
skSocket = tlListen1.AcceptSocket();//接受远程机的连接请求,并获得用以接收数据的Socket实例
EndPoint tempRemoteEP = skSocket.RemoteEndPoint;//获得远程计算机对应的网络远程终结点
IPEndPoint tempRemoteIP = (IPEndPoint)tempRemoteEP;
IPHostEntry host = Dns.GetHostByAddress(tempRemoteIP.Address);
string HostName = host.HostName;//根据获得的远程机的网络远程终结点获得远程计算机的名称
statusBar1.Panels[1].Text = "'" + HostName + "'" + "远程计算机正确连接!";
while (listenerRun) //循环侦听
{
Byte[] stream = new Byte[80]; //定义从远程计算机接收到数据存放的数据缓冲区
string time = DateTime.Now.ToString();//获得当前的时间
//接收数据,并存放到定义的缓冲区中
int i = skSocket.ReceiveFrom(stream, ref tempRemoteEP);
//以指定的编码,从缓冲区中解析出内容
string sMessage = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(stream);
listBox2.Items.Add("(" + time + ") " + HostName + ":");
listBox2.Items.Add(sMessage); //显示接收到的数据
}
}
catch (System.Security.SecurityException)
{
MessageBox.Show("防火墙安全错误!", "错误", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation);
}
}
//侦听端口
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
th = new Thread(new ThreadStart(Listen));//以Listen过程来初始化线程实例
th.Start();//启动此线程
this.button2.Enabled = false;
}
//发送信息
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string sMsg = textBox4.Text;
string MyName = Dns.GetHostName();
//以特定的编码往向数据流中写入数据,默认为UTF8Encoding 的实例
reqStreamW = new StreamWriter(tcpStream);
reqStreamW.Write(sMsg); //将字符串写入数据流中
reqStreamW.Flush();//清理当前编写器的所有缓冲区,并使所有缓冲数据写入基础流
string time = DateTime.Now.ToString();
listBox1.Items.Add("(" + time + ") " + MyName + ":");//显示传送的数据和时间
listBox1.Items.Add(sMsg);
textBox4.Clear();
}
catch //异常处理
{
statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "无法发送信息到目标计算机!";
}
}
//断开连接
private void button4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
listenerRun = false;
tcpc.Close();
statusBar1.Panels[0].Text = "断开连接!";
button1.Enabled = true;
button2.Enabled = false;
button4.Enabled = false;
}