C#处理文本文件
文本文件是一种常用的文件格式,所以如何处理文本文件也就成为编程的一个重点。本文就来探讨一下用C#是如何来处理文本文件。其内容重点就是如何读取文本文件内容、如何改变文本文件的内容,以及如何用C#来实现对读取后的文本文件的打印预览和打印。
(1).如何读取文本文件内容:
在本文介绍的程序中,是把读取的文本文件,用一个richTextBox组件显示出来。要读取文本文件,必须使用到"StreamReader"类,这个类是由名字空间"System.IO"中定义的。通过"StreamReader"类的"ReadLine()"方法,就可以读取打开数据流当前行的数据了。下面代码实现的功能就是读取"C:\file.txt"并在richTextBox1组件中显示出来:
FileStream fs = new FileStream("C:\\file.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader m_streamReader = new StreamReader(fs);
//使用StreamReader类来读取文件
m_streamReader.BaseStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
// 从数据流中读取每一行,直到文件的最后一行,并在richTextBox1中显示出内容
this.richTextBox1.Text = "";
string strLine = m_streamReader.ReadLine();
while (strLine != null)
{
this.richTextBox1.Text += strLine + "\n";
strLine = m_streamReader.ReadLine();
}
//关闭此StreamReader对象
m_streamReader.Close();
其实现的功能如下图:
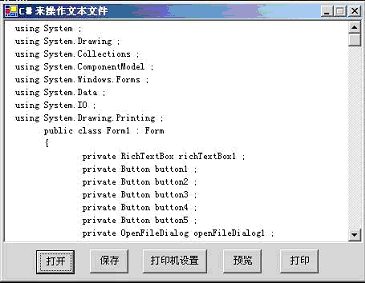
图01:读取文本文件并显示出来
(2).如何改变文本文件中数据内容:
在本文介绍的程序中,改变文本文件数据内容的功能是通过改变richTextBox1中的内容来实现的,当richTextBox1这的内容改变后,按动"另存为",就把richTextBox1中内容存储到指定的文本文件中了。要想改变文本文件内容,要使用到"StreamWriter"类,这个类和"StreamReader"一样,都是由"System.IO"名字空间来定义的。通过"StreamWriter"类的"Write()"方法,就可以轻松实现文本文件内容的更改了。下面代码的功能是:如果"C"盘存在"file.txt",则把richTextBox1中的内容写入到"file.txt"中,如果不存在,则创建此文件,然后在写入文本数据。
//创建一个文件流,用以写入或者创建一个StreamWriter
FileStream fs = new FileStream("C\\file.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter m_streamWriter = new StreamWriter(fs);
m_streamWriter.Flush();
// 使用StreamWriter来往文件中写入内容
m_streamWriter.BaseStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
// 把richTextBox1中的内容写入文件
m_streamWriter.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
//关闭此文件
m_streamWriter.Flush();
m_streamWriter.Close();
从上面这二个代码可以,写入数据比起读取数据要显得容易些。
(3).如何实现打印预览:
打印预览是通过打印预览对话框来实现的,实现对读取得文本文件的打印预览,最为重要的就是要通知打印预览对话框所要预览的文件的内容。下面代码就是把richTextBox1中显示的内容,通过打印预览对话框显示出来:
string strText = richTextBox1.Text;
StringReader myReader = new StringReader(strText);
PrintPreviewDialog printPreviewDialog1 = new PrintPreviewDialog();
printPreviewDialog1.Document = ThePrintDocument;
printPreviewDialog1.FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.Fixed3D;
printPreviewDialog1.ShowDialog();
其实现的功能的如下图:
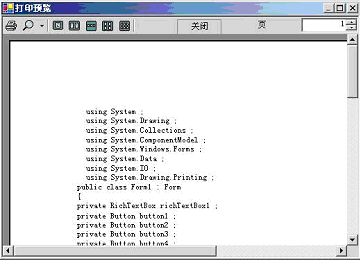
图02:对文本文件实现打印预览
(4).如何打印文件:
在名字空间"System.Drawing.Printing"中定义了一个类"PrintDocument",通过调用此类的"Print"方法就可以触发在此名字空间中封装的另外一个事件"PrintPage"。在此事件中设定要打印的文档内容,从而实现队文本文件的打印操作。下面代码是调用"PrintDocument"的"Print"方法,和调用事件"PrintPage"来打印richTextBox1中的内容:
ThePrintDocument.Print ( ) ;//其中ThePrintDocument是"PrintDocument"类的一个对象
下列代码是设定打印内容即打印richTextBox1中的内容:
float linesPerPage = 0;
float yPosition = 0;
int count = 0;
float leftMargin = ev.MarginBounds.Left;
float topMargin = ev.MarginBounds.Top;
string line = null;
Font printFont = richTextBox1.Font;
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black);
//计算每一页打印多少行
linesPerPage = ev.MarginBounds.Height / printFont.GetHeight(ev.Graphics);
//重复使用StringReader对象 ,打印出richTextBox1中的所有内容
while (count < linesPerPage && ((line = myReader.ReadLine()) != null))
{
// 计算出要打印的下一行所基于页面的位置
yPosition = topMargin + (count * printFont.GetHeight(ev.Graphics));
// 打印出richTextBox1中的下一行内容
ev.Graphics.DrawString(line, printFont, myBrush, leftMargin, yPosition, new StringFormat());
count++;
}
// 判断如果还要下一页,则继续打印
if (line != null)
ev.HasMorePages = true;
else
ev.HasMorePages = false;
myBrush.Dispose();
注释:由于在上述的代码中省掉了这些类所对于地名字空间,所以要想成功的编译和运行上述代码,就要在程序头部要导入所使用的名字空间。
三. 用C#处理文本文件的完整源程序代码(control.cs)
掌握了上面这些关键步骤,就可以方便的得到用C#来处理文本文件的一个完整的源程序,具体如下:
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data;
using System.IO;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
public class Form1 : Form
{
private RichTextBox richTextBox1;
private Button button1;
private Button button2;
private Button button3;
private Button button4;
private Button button5;
private OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1;
private SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog1;
private PrintDialog printDialog1;
private PrintDocument ThePrintDocument;
private PrintPreviewDialog printPreviewDialog1;
private StringReader myReader;
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
public Form1()
{
//初始化窗体中的各个组件
InitializeComponent();
}
//清除程序中使用多的资源
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
if (components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
richTextBox1 = new RichTextBox();
button1 = new Button();
button2 = new Button();
button3 = new Button();
button4 = new Button();
button5 = new Button();
saveFileDialog1 = new SaveFileDialog();
openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
printPreviewDialog1 = new PrintPreviewDialog();
printDialog1 = new PrintDialog();
ThePrintDocument = new PrintDocument();
ThePrintDocument.PrintPage += new PrintPageEventHandler(ThePrintDocument_PrintPage);
SuspendLayout();
richTextBox1.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
richTextBox1.Name = "richTextBox1";
richTextBox1.Size = new Size(448, 280);
richTextBox1.TabIndex = 0;
richTextBox1.Text = "";
button1.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
button1.Location = new Point(41, 289);
button1.Name = "button1";
button1.Size = new Size(48, 30);
button1.TabIndex = 1;
button1.Text = "打开";
button1.Click += new System.EventHandler(button1_Click);
button2.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
button2.Location = new Point(274, 288);
button2.Name = "button2";
button2.Size = new Size(48, 30);
button2.TabIndex = 4;
button2.Text = "预览";
button2.Click += new System.EventHandler(button2_Click);
button3.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
button3.Location = new Point(108, 288);
button3.Name = "button3";
button3.Size = new Size(48, 30);
button3.TabIndex = 2;
button3.Text = "保存";
button3.Click += new System.EventHandler(button3_Click);
button4.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
button4.Location = new Point(174, 288);
button4.Name = "button4";
button4.Size = new Size(80, 30);
button4.TabIndex = 3;
button4.Text = "打印机设置";
button4.Click += new System.EventHandler(button4_Click);
button5.Anchor = AnchorStyles.None;
button5.Location = new Point(345, 288);
button5.Name = "button5";
button5.Size = new Size(48, 30);
button5.TabIndex = 5;
button5.Text = "打印";
button5.Click += new System.EventHandler(button5_Click);
saveFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "*.txt";
saveFileDialog1.FileName = "file.txt";
saveFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = "c:\\";
saveFileDialog1.Title = "另存为!";
openFileDialog1.DefaultExt = "*.txt";
openFileDialog1.FileName = "file.txt";
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory = "c:\\";
openFileDialog1.Title = "打开文本文件!";
AutoScaleBaseSize = new Size(6, 14);
ClientSize = new Size(448, 325);
this.Controls.Add(button1);
this.Controls.Add(button2);
this.Controls.Add(button3);
this.Controls.Add(button4);
this.Controls.Add(button5);
this.Controls.Add(richTextBox1);
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.Name = "Form1";
this.Text = "C#来操作文本文件";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(openFileDialog1.FileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader m_streamReader = new StreamReader(fs);
//使用StreamReader类来读取文件
m_streamReader.BaseStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
// 从数据流中读取每一行,直到文件的最后一行,并在richTextBox1中显示出内容
this.richTextBox1.Text = "";
string strLine = m_streamReader.ReadLine();
while (strLine != null)
{
this.richTextBox1.Text += strLine + "\n";
strLine = m_streamReader.ReadLine();
}
//关闭此StreamReader对象
m_streamReader.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception em)
{
Console.WriteLine(em.Message.ToString());
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
//获得另存为的文件名称
if (saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
//创建一个文件流,用以写入或者创建一个StreamWriter
FileStream fs = new FileStream(@saveFileDialog1.FileName, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter m_streamWriter = new StreamWriter(fs);
m_streamWriter.Flush();
// 使用StreamWriter来往文件中写入内容
m_streamWriter.BaseStream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
// 把richTextBox1中的内容写入文件
m_streamWriter.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
//关闭此文件
m_streamWriter.Flush();
m_streamWriter.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception em)
{
Console.WriteLine(em.Message.ToString());
}
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
printDialog1.Document = ThePrintDocument;
printDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
//预览打印文档
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
try
{
string strText = richTextBox1.Text;
myReader = new StringReader(strText);
PrintPreviewDialog printPreviewDialog1 = new PrintPreviewDialog();
printPreviewDialog1.Document = ThePrintDocument;
printPreviewDialog1.FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.Fixed3D;
printPreviewDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
Console.WriteLine(exp.Message.ToString());
}
}
//打印richTextBox1中的内容
private void button5_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
printDialog1.Document = ThePrintDocument;
string strText = richTextBox1.Text;
myReader = new StringReader(strText);
if (printDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
ThePrintDocument.Print();
}
}
protected void ThePrintDocument_PrintPage(object sender, PrintPageEventArgs ev)
{
float linesPerPage = 0;
float yPosition = 0;
int count = 0;
float leftMargin = ev.MarginBounds.Left;
float topMargin = ev.MarginBounds.Top;
string line = null;
Font printFont = richTextBox1.Font;
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black);
//计算每一页打印多少行
linesPerPage = ev.MarginBounds.Height / printFont.GetHeight(ev.Graphics);
//重复使用StringReader对象 ,打印出richTextBox1中的所有内容
while (count < linesPerPage && ((line = myReader.ReadLine()) != null))
{
// 计算出要打印的下一行所基于页面的位置
yPosition = topMargin + (count * printFont.GetHeight(ev.Graphics));
// 打印出richTextBox1中的下一行内容
ev.Graphics.DrawString(line, printFont, myBrush, leftMargin, yPosition, new StringFormat());
count++;
}
// 判断如果还要下一页,则继续打印
if (line != null)
ev.HasMorePages = true;
else
ev.HasMorePages = false;
myBrush.Dispose();
}
}
四.总结
本文虽然只是介绍了用C#处理文本文件,但其实对C#处理其他文件也有很多的参考价值,这是因为在名字空间"System.IO"中定义的用以处理其他文件的类的结构和用以处理文本文件的类的结构有很多是相同的。希望本文对你用C#进行文件方面的编程有所帮助。
(责任编辑 赵正北)